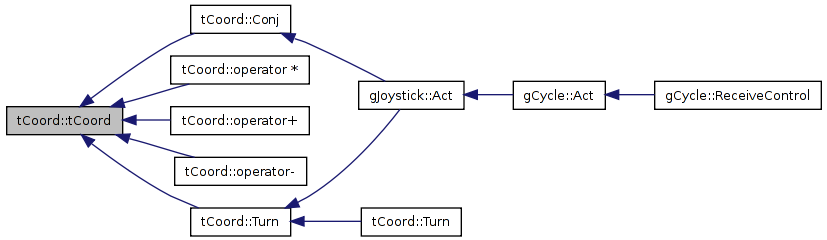
Definition at line 43 of file tCoord.h.
Referenced by Conj(), operator *(), operator+(), operator-(), and Turn().
#include <tCoord.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| tCoord (REAL X=0, REAL Y=0) | |
| bool | operator== (const tCoord &a) const |
| Default constructor. | |
| bool | operator!= (const tCoord &a) const |
| Are the two coordinates far apart from each other to be considered different? | |
| tCoord | operator- (const tCoord &a) const |
| substracts two coordinates | |
| tCoord | operator- () const |
| mirrors a coordinate around the x and y axis | |
| tCoord | operator+ (const tCoord &a) const |
| adds two coordinates | |
| const tCoord & | operator+= (tCoord const &other) |
| adds two coordinates | |
| const tCoord & | operator-= (tCoord const &other) |
| substracts two coordinates | |
| tCoord | operator * (REAL a) const |
| stretches a coordinate by a factor from the center | |
| const tCoord & | operator *= (REAL a) |
| stretches a coordinate by a factor from the center | |
| const tCoord & | operator *= (tCoord const &other) |
| stretches a coordinate by a factor from the center | |
| REAL | NormSquared () const |
| returns the square of the distance to the origin | |
| REAL | Norm () const |
| returns the distance to the orign | |
| void | Normalize () |
| normalizes the coordinate by setting the distance to the orign to 1 and keeping the ratio of the x and y coordinates | |
| const tCoord & | operator= (const tCoord &a) |
| overwrites a coordinate with another one | |
| REAL | operator * (const tCoord &a) const |
| tCoord | Turn (const tCoord &a) const |
| complex multiplication: turns this by angle given in a | |
| tCoord | Turn (REAL x, REAL y) const |
| complex multiplication: turns this by angle given in x and y | |
| tCoord | Conj () const |
| complex conjugation | |
| void | Print (std::ostream &s) const |
| Prints the coordinate into a stream (format: "(x,y)"). | |
| void | Read (std::istream &s) |
| Reads the coordinate from a stream (format: "(x,y)"). | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static REAL | F (const tCoord &a, const tCoord &b) |
| scalar product | |
| static REAL | V (const tCoord &a, const tCoord &b, const tCoord &c) |
| static REAL | CrossProduct (tCoord const &a, tCoord const &b, tCoord const &c) |
| returns the cross product of the three given points, whatever that is--code taken from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graham_scan | |
| static REAL | Tangent (tCoord const &a, tCoord const &b) |
| returns delta y over delta x | |
| template<typename T> | |
| static void | GrahamScan (T &in, T &out) |
| finds the smallest convex polygon completely surrounding all points in in and stores them in out. See also http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graham_scan | |
Public Attributes | |
| REAL | x |
| REAL | y |
| the stored coordinates | |
Classes | |
| class | GrahamComparator |
Definition at line 40 of file tCoord.h.
Definition at line 43 of file tCoord.h.
Referenced by Conj(), operator *(), operator+(), operator-(), and Turn().

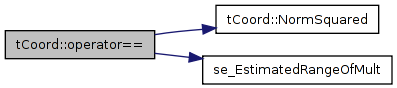
| bool tCoord::operator== | ( | const tCoord & | a | ) | const [inline] |
Default constructor.
Are the two coordinates close enough to each other to be considered equeal?
| a | the other coordinate |
Definition at line 136 of file tCoord.h.
References EPS, NormSquared(), and se_EstimatedRangeOfMult().
Referenced by operator!=().
00136 { 00137 return ((*this-a).NormSquared()<=(EPS*EPS)*se_EstimatedRangeOfMult(*this,a)); 00138 }

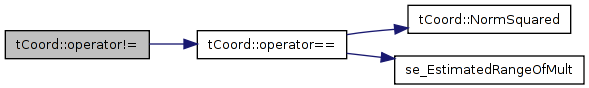
| bool tCoord::operator!= | ( | const tCoord & | a | ) | const [inline] |
Are the two coordinates far apart from each other to be considered different?
Definition at line 47 of file tCoord.h.
References operator==().
| tCoord tCoord::operator- | ( | ) | const [inline] |
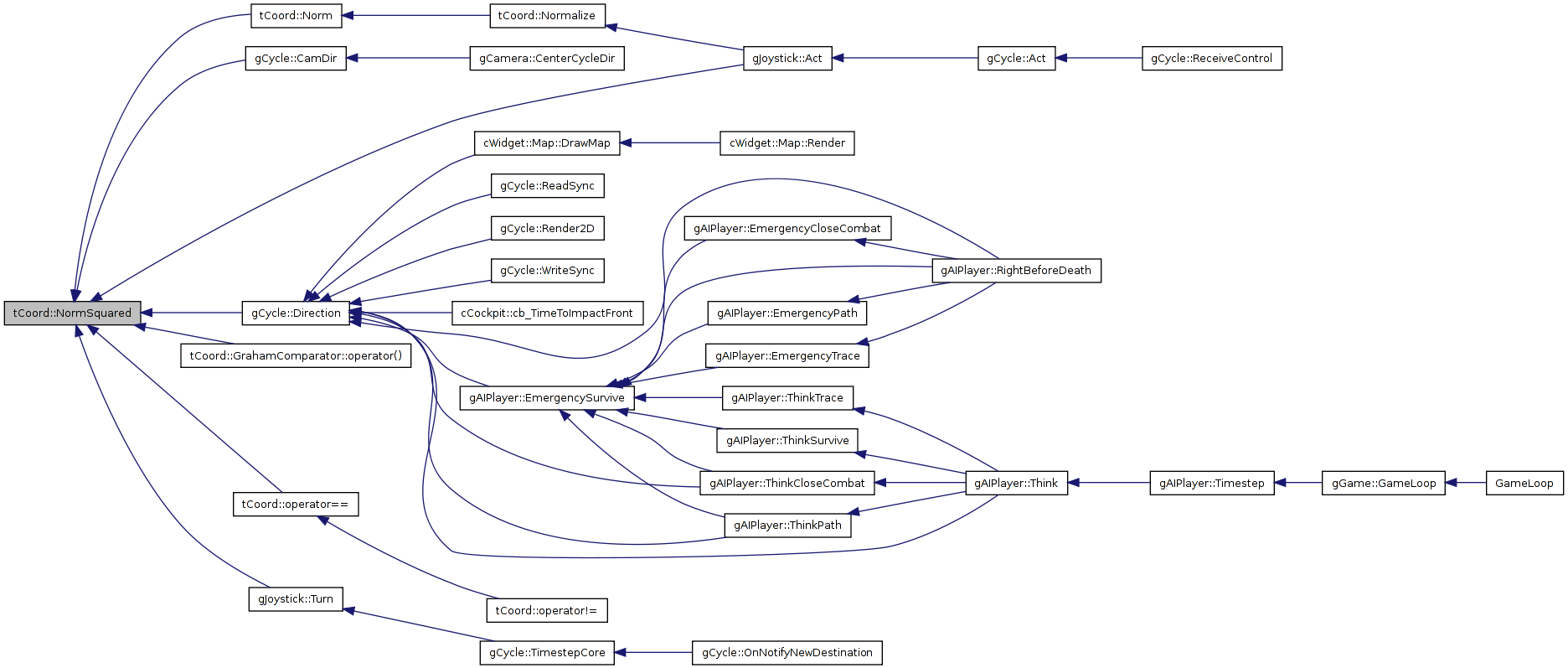
| REAL tCoord::NormSquared | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns the square of the distance to the origin
Definition at line 56 of file tCoord.h.
Referenced by gJoystick::Act(), gCycle::CamDir(), gCycle::Direction(), Norm(), tCoord::GrahamComparator::operator()(), operator==(), and gJoystick::Turn().
| REAL tCoord::Norm | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns the distance to the orign
Definition at line 57 of file tCoord.h.
References NormSquared(), and sqrt().
Referenced by Normalize().

| void tCoord::Normalize | ( | ) | [inline] |
normalizes the coordinate by setting the distance to the orign to 1 and keeping the ratio of the x and y coordinates
Definition at line 58 of file tCoord.h.
References Norm().
Referenced by gJoystick::Act().


| static REAL tCoord::CrossProduct | ( | tCoord const & | a, | |
| tCoord const & | b, | |||
| tCoord const & | c | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
returns the cross product of the three given points, whatever that is--code taken from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graham_scan
Definition at line 75 of file tCoord.h.
Referenced by GrahamScan().

| void tCoord::GrahamScan | ( | T & | in, | |
| T & | out | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
finds the smallest convex polygon completely surrounding all points in in and stores them in out. See also http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graham_scan
| in | the standard container containing the tCoords to wrap into a rubber band. In will be modified! | |
| out | the standard container to put the rubber band into, its contents will be erased |
Definition at line 163 of file tCoord.h.
References CrossProduct(), EPS, tASSERT, x, and y.
Referenced by eWallRim::UpdateBounds().
00163 { 00164 tASSERT(!in.empty()); 00165 out.clear(); 00166 00167 // find the point that's closest to the bottom, preferring points to the left 00168 tCoord P=in.front(); 00169 typename T::iterator iter(in.begin()+1); 00170 for(; iter != in.end(); ++iter) { 00171 if(iter->y < P.y || iter->y == P.y && iter->x < P.x) { 00172 P = *iter; 00173 } 00174 } 00175 00176 std::sort(in.begin(), in.end(), GrahamComparator(P)); 00177 00178 //std::cerr << "P: " << P << std::endl; 00179 00180 out.push_back(P); 00181 for(typename T::iterator iter = in.begin()+1; iter != in.end(); ++iter) { 00182 if(*iter != P) { 00183 out.push_back(*iter); 00184 break; 00185 } 00186 } 00187 if(out.size()<2) return; //all points equeal P, kinda boring... 00188 00189 //std::copy(in.begin(), in.end(), std::ostream_iterator<tCoord>(std::cerr, " ")); 00190 //std::cerr << std::endl; 00191 for(typename T::iterator iter = in.begin(); iter != in.end(); ++iter) { 00192 //std::cerr << "New point: " << *iter << "; angle=" << (atanf(Tangent(P, *iter))*180/M_PI) << std::endl; 00193 } 00194 00195 for(typename T::iterator iter = in.begin()+2; iter != in.end(); ++iter) { 00196 if(*iter == P) continue; 00197 if(*iter == *(iter - 1)) continue; //duplicate or near- duplicate point; We don't want that mess. 00198 //std::cerr << "New point: " << *iter << "; angle=" << Tangent(P, *iter) << std::endl; 00199 //if(iter->y > 200) std::cerr << "==================\n"; 00200 float product = CrossProduct(out[out.size()-2], out.back(), *iter); 00201 if (product < 0 || fabs(product) < EPS) { 00202 //the last three points are concave, remove points until they're not 00203 while((product < 0 || fabs(product) < EPS) && out.size() > 2) { 00204 //std::cerr << "concave: " << *(iter-2) << " " << *(iter-1) << " " << *iter << std::endl; 00205 //std::copy(out.begin(), out.end(), std::ostream_iterator<tCoord>(std::cerr, " ")); 00206 //std::cerr << std::endl; 00207 out.pop_back(); 00208 product = CrossProduct(out[out.size()-2], out.back(), *iter); 00209 } 00210 } else { 00211 //std::cerr << "Passed point: " << *iter << std::endl; 00212 } 00213 out.push_back(*iter); 00214 //std::copy(out.begin(), out.end(), std::ostream_iterator<tCoord>(std::cerr, " ")); 00215 //std::cerr << std::endl; 00216 } 00217 float product = CrossProduct(out[out.size()-2], out.back(), P); 00218 while((product < 0 || fabs(product) < EPS) && out.size() > 2) { 00219 //std::cerr << "concave: " << *(iter-2) << " " << *(iter-1) << " " << *iter << std::endl; 00220 //std::copy(out.begin(), out.end(), std::ostream_iterator<tCoord>(std::cerr, " ")); 00221 //std::cerr << std::endl; 00222 out.pop_back(); 00223 product = CrossProduct(out[out.size()-2], out.back(), P); 00224 } 00225 //std::cerr << "=====\n"; 00226 //for(typename T::iterator iter = out.begin(); iter != out.end(); ++iter) { 00227 // std::cerr << *iter << std::endl; 00228 //} 00229 00230 }


| tCoord tCoord::Conj | ( | ) | const [inline] |
| void tCoord::Print | ( | std::ostream & | s | ) | const |
Prints the coordinate into a stream (format: "(x,y)").
Referenced by operator<<().

| void tCoord::Read | ( | std::istream & | s | ) |
Reads the coordinate from a stream (format: "(x,y)").
Referenced by operator>>().

Definition at line 42 of file tCoord.h.
Referenced by gJoystick::ActInternal(), rFontContainer::BBox(), cWidget::Map::ClipperCircle::Begin(), cWidget::Map::ClipperRect::Begin(), cWidget::Map::ClipperCircle::Clip(), Conj(), CrossProduct(), display_cockpit_lucifer(), rGradient::DrawAt(), cWidget::Map::DrawMap(), cWidget::Map::DrawRimWalls(), F(), rGradient::GetGradientPt(), GrahamScan(), zShapePolygon::isInside(), NormSquared(), operator *(), operator *=(), operator+(), operator+=(), operator-(), operator-=(), operator=(), cWidget::WithCoordinates::Process(), cWidget::WithColorFunctions::ProcessGradient(), cWidget::Rectangle::Render(), cWidget::Map::Render(), cWidget::Label::Render(), rFontContainer::Render(), gCycle::Render2D(), cWidget::VerticalBarGauge::RenderCaption(), cWidget::BarGauge::RenderCaption(), cWidget::NeedleGauge::RenderGraph(), cWidget::VerticalBarGauge::RenderGraph(), cWidget::BarGauge::RenderGraph(), cWidget::BarGauge::RenderMinMax(), rGradient::SetGradientEdges(), rGradient::SetValues(), Tangent(), and Turn().
the stored coordinates
Definition at line 42 of file tCoord.h.
Referenced by gJoystick::ActInternal(), rFontContainer::BBox(), cWidget::Map::ClipperCircle::Begin(), cWidget::Map::ClipperRect::Begin(), cWidget::Map::ClipperCircle::Clip(), Conj(), CrossProduct(), display_cockpit_lucifer(), rGradient::DrawAt(), cWidget::Map::DrawMap(), cWidget::Map::DrawRimWalls(), F(), rGradient::GetGradientPt(), GrahamScan(), zShapePolygon::isInside(), NormSquared(), operator *(), operator *=(), operator+(), operator+=(), operator-(), operator-=(), operator=(), cWidget::WithCoordinates::Process(), cWidget::WithColorFunctions::ProcessGradient(), cWidget::Rectangle::Render(), cWidget::Map::Render(), cWidget::Label::Render(), rFontContainer::Render(), gCycle::Render2D(), cWidget::VerticalBarGauge::RenderCaption(), cWidget::BarGauge::RenderCaption(), cWidget::NeedleGauge::RenderGraph(), cWidget::VerticalBarGauge::RenderGraph(), cWidget::BarGauge::RenderGraph(), cWidget::BarGauge::RenderMinMax(), cWidget::WithCoordinates::SetFactor(), rGradient::SetGradientEdges(), rGradient::SetValues(), Tangent(), and Turn().
 1.5.4
1.5.4